Abstract
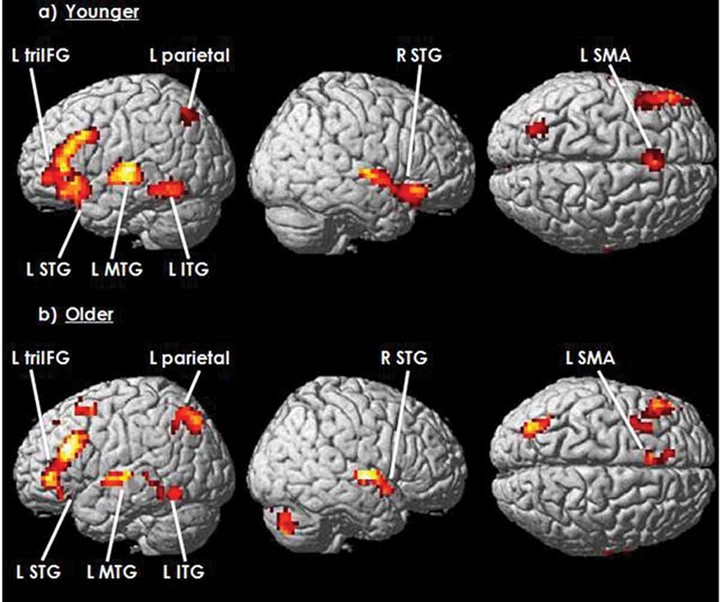
The efficacy of listening comprehension is presumably sustained over the life span, contradicting the stereotype of universal cognitive decline. It is thus worth investigating whether and how the preserved auditory semantic function is supported by affected or unaffected neural mechanism with age. To investigate this issue, 22 younger and 21 older Japanese adults were imaged in a 3 Tesla MRI scanner while performing an auditory semantic-tone task. Results showed that (a) relative to younger adults, older participants had preserved accuracy and slowed responses, underpinned by weakened interconnectivity and largely unchanged activation and laterality; (b) older adults with superior performance developed increased regional left-lateralization and stronger interregional connectivity within the domain-general networks; (c) these age-related or performance-related cortical reorganizations were largely consistent with neurocognitive aging models that were supported by age-sensitive cognitive domains, suggesting that these models might also be accountable for relatively age-intact cognitive functions such as auditory semantic processing.